For example in the medication study the effect is the mean difference between the treatment and control groups. These measurements are not replicates.
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
Therefore every independent measures study can have problems with the internal validity of the results and the reliability of the results.

. The distinction is very simple. However the disadvantage of independent measures design is that there is the potential for error due to individual differences between the groups of participants. Again a repeated measures ANOVA has at least 1.
Repeated measures means exactly the same thing as within subjects. When you think of a typical experiment you probably picture an experimental design that uses mutually exclusive independent groups. Or 3 conditions 4 conditions are different people.
The benefits of using independent measures in this research allows a comparison between the abilities of children. Quicker and cheaper. The observations within each sample must be independent see p.
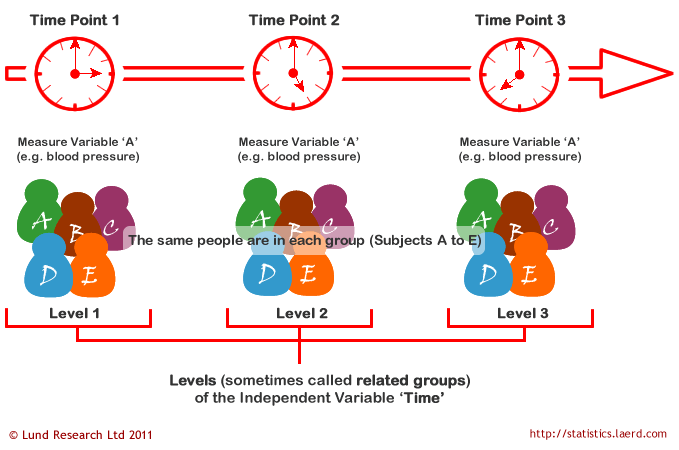
In contrast to an independent measures design a repeated measures design has only one group of participants who complete every research condition. Repeated measures designs also known as a within-subjects designs can seem like oddball experiments. Where measurements are repeated over time such as when measuring changes in blood pressure due to an exercise-training programme the independent variable is time.
Fewer subjects need to be recruited trained and compensated to complete an entire experiment. A short time series is observed for each observation. It means that the same subjects were measured in several different conditions.
A researcher is using an independent-measures design to evaluate the difference. In repeated measures data the dependent variable is measured more than once for each subject. This constrained repeated measure model performs comparably to ANCOVA model.
The F -statistic is calculated as below. The table shows the p p -value associated with our F F -value. They are the same people.
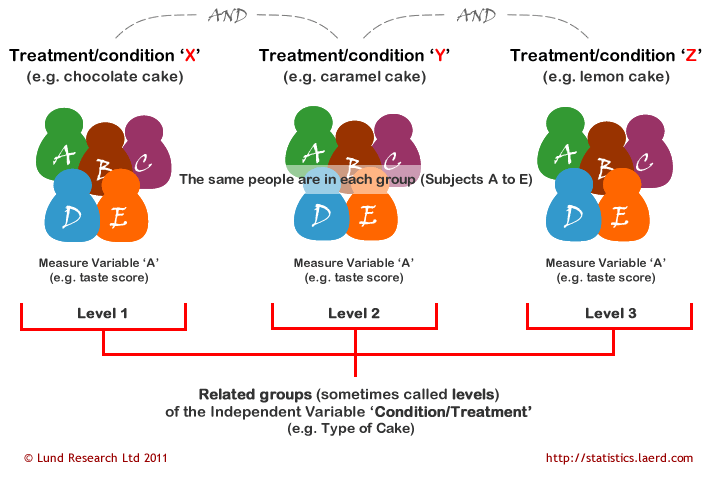
Independent measures involve using two separate groups of participants. The advantage of this is that individual differences between participants are removed as a potential confounding variable. Repeated-measures design means that the same sample is tested in all of the different treatments.
One in each condition. In a repeated measures case the same subjects are being tested under different conditions. The repeated measures ANOVA compares means across one or more variables that are based on repeated observations.
The term repeated measures refers to experimental designs or observational studies in which each experimental unit or subject is measured at several points in time. The two populations from which the samples are selected must have equal. Repeated measures was used because the children in each age group participated in three different conditions across three types of task.
The term longitudinal data is also used for this type of data. Measuring the mean scores of subjects during three or more time points. For example suppose that a silicon wafer is etched in a single-wafer plasma etching process and a critical dimension on this wafer is measured three times.
Here it is again. Independent measures was used so that different age groups of children could participate within the research. More people are needed than with the repeated measures design ie more time consuming.
Avoids order effects such as practice or fatigue as people participate in one condition only. We might write up the results of our experiment and say that the main effect condition was not significant F 24 0812 MSE 4433 p 0505. Statistics and Probability questions and answers.
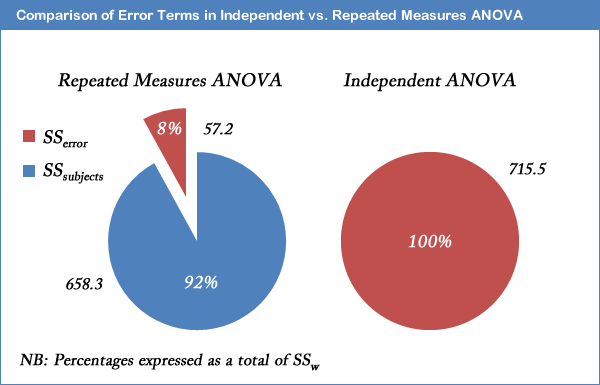
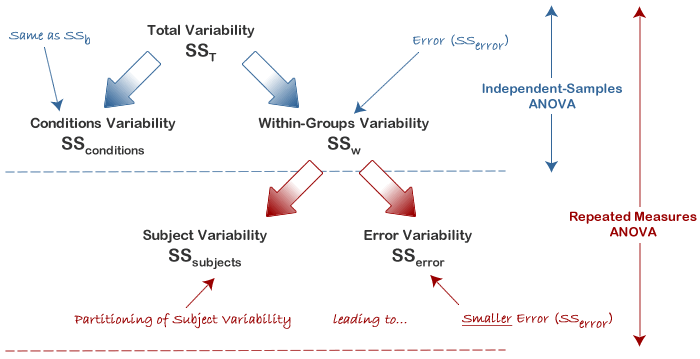
They are a form of repeated measurements and in this case the observed variability in the three. Individual differences are eliminated or removed from the variances in the F-ratio for the repeated measures ANOVA whereas individual differences are a part of the variance in the numerator and in the denominator of the F-ratio for the independent-measures ANOVA. For example if an independent groups design requires 20 subjects per experimental group a repeated measures design may only require 20 total.
This answer is not useful. A repeated measures ANOVA model can also include zero or more independent variables. Independent-measures design or between-subjects design means that there is a separate sample for each of the treatments being compared.
Usually there is some independent variable often called a within-subject factor that changes with each measurement. 1 The difference between repeated measures and independent measures designs Experimental designs with ---------------are called independent measures designs Experimental designs with ---------------are called repeated measures. In repeated measures ANOVA the independent variable has categories called levels or related groups.
There is an important distinction between replication and repeated measurements. We already conducted the repeated-measures ANOVA using R and reported the ANOVA. The focus is on comparing group properties rather than individuals.
They are tests for the difference in mean scores. Each level or related group is a specific time point. Show activity on this post.
Experimental units are randomly allocated to one of g treatments. There is no ordering to the subjects within the group so their responses should be equally correlated. You will already have been familiarised with SS conditions from earlier in this guide but in some of the calculations in the preceding sections you will see SS conditions.
If a person is involved in several conditions they may become bored tired. All ANOVAs compare one or more mean scores with each other. Studies that use independent samples estimate between-subject effects.
The two populations from which the samples are selected must be normal. Instead if you really want to model both pre- and post-treatment scores you can use a constrained repeated measure model time timegroup by forcing the intercept or difference in baseline score between two groups equal to 0. These effects are the differences between groups such as the mean difference.
The repeated measures ANOVA like other ANOVAs generates an F -statistic that is used to determine statistical significance. In ANOVA terminology these conditions form a repeated measures factor or equivalently a within subjects factor. A repeated measures ANOVA is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of three or more groups in which the same subjects show up in each group.
With respect to these two designs ANOVA is very similar to t-tests. These experiments have a control group and treatment groups that have clear divisions between them. A repeated measures ANOVA is typically used in two specific situations.
Hence for the exercise-training study there would be. In an independent groups test the subjects in the 2 groups or conditions t test or 3 groups 4 groups 5 groups. A repeated measures design consists of testing the same individuals on two or more conditions.
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics
0 Comments